Brain-derived Tau mAb 2B8
Exhibitor
Roboscreen GmbH
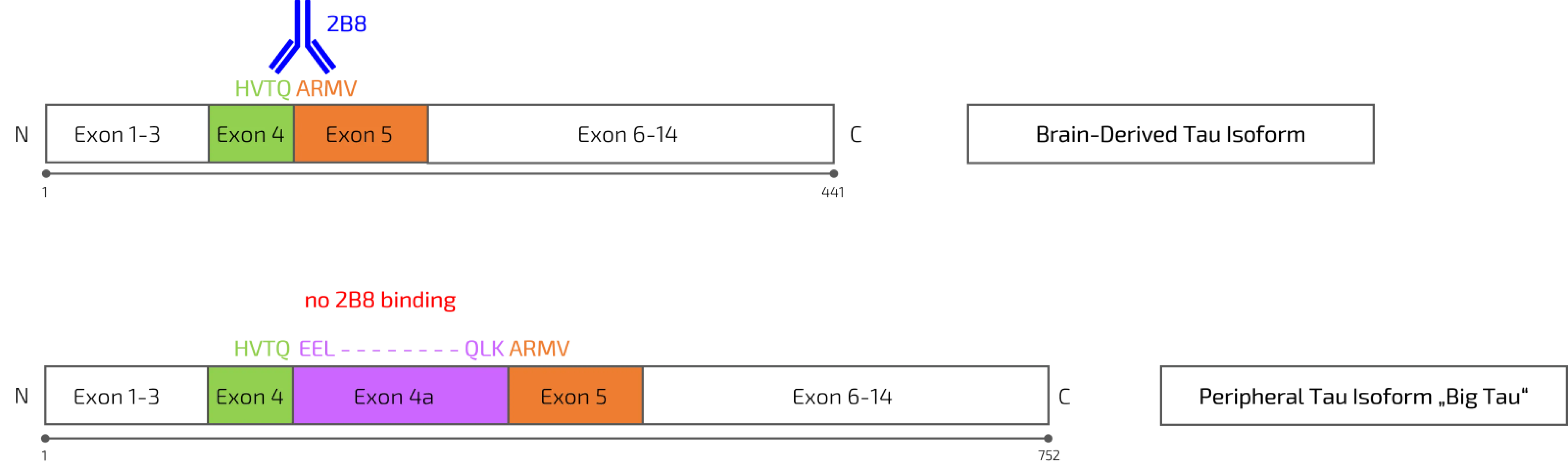
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein highly expressed in neurons, where it plays a critical role in microtubule stabilization and axonal transport. Brain-derived Tau originates from the central nervous system and reflects neuronal physiology and pathology, including neurodegenerative processes associated with tauopathies. In contrast, peripheral Tau is expressed by non-neuronal tissues and includes longer “Big-Tau” isoforms that contain the exon 4a insert, which are not representative of CNS pathology.
Conventional blood-based Tau measurements capture a heterogeneous mixture of central and peripheral Tau species, thereby limiting their specificity for brain-derived signals. To address this challenge, we have developed the monoclonal antibody 2B8 that selectively recognizes continuous exon 4–5 sequences present in brain-derived Tau isoforms, while showing no binding to peripheral Tau variants containing the exon 4a insert. This molecular specificity enables the selective detection of CNS-derived Tau in blood-based samples.